Segmental Wall Overview |

|

|
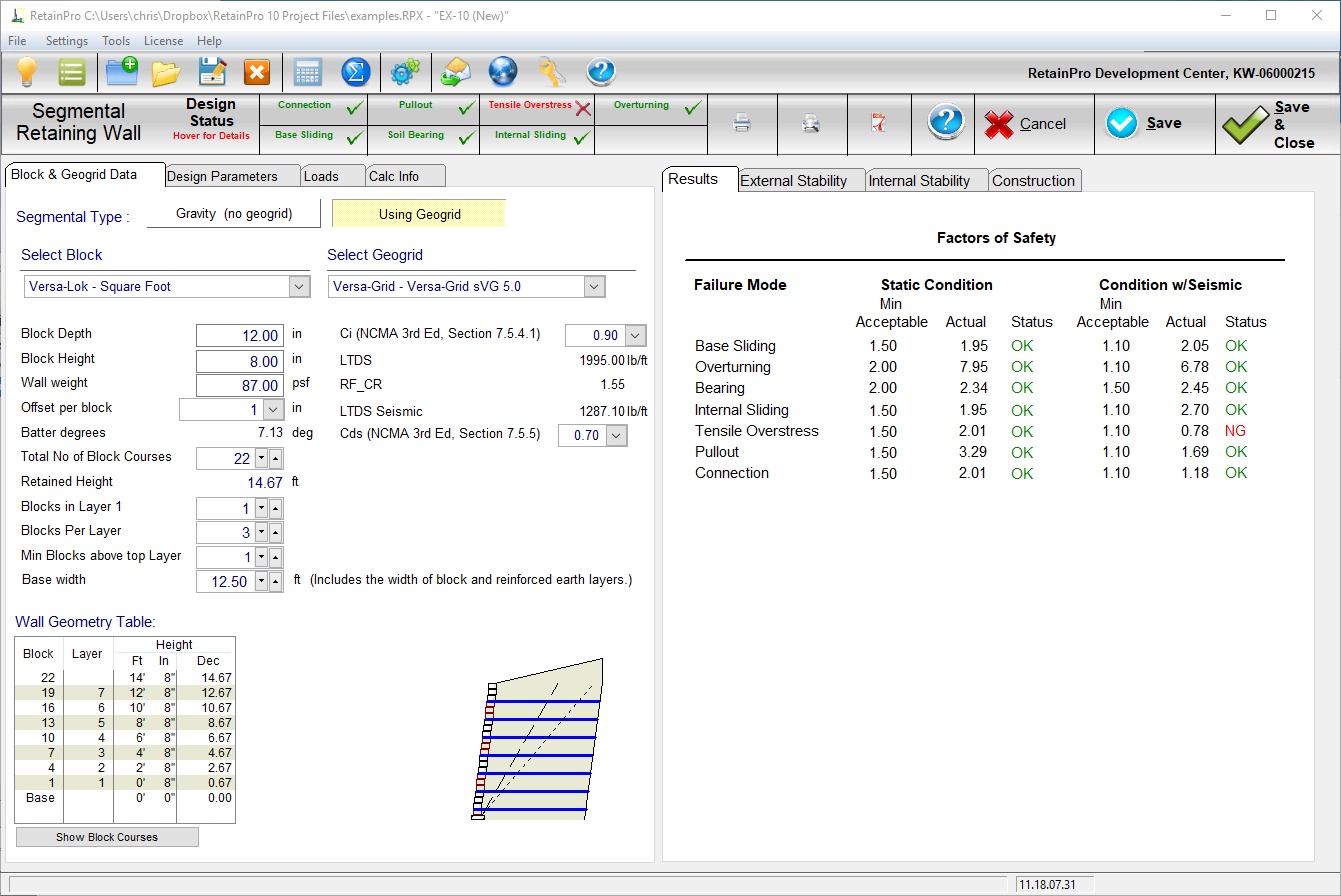
Segmental Wall Overview
Segmental walls are constructed of stacked masonry blocks, usually of proprietary configurations, without steel rebar, grouting, or mortar. They are dry-stacked, either vertically or with offsets at each block such that the wall is slightly battered and leans into the earth. When geogrids are used in segmental retaining walls, they are placed in horizontal layers separated by some vertical distance as the wall is constructed and backfilling progresses. Their purpose is to reinforce the earth behind the wall such that the reinforced earth zone acts en masse with the wall to resist sliding and overturning, hence no conventional foundation is required. (These walls are also called MSE – Mechanically Stabilized Earth walls.) The geogrids extend beyond the failure plane and resist pullout by friction resistance due to the weight of soil above. Connection to the wall blocks is achieved through friction between blocks and sometimes by proprietary connection devices.